Horizontal HRSG is recognized as one of the most advanced heat recovery systems used in power plants and heavy industries to enhance thermal efficiency and deliver stable steam production. This article outlines how the horizontal configuration—supported by optimized tube arrangements, cold-casing construction, modular architecture, and reliable operating performance—maximizes its integration with modern gas turbines. It also explores its industrial applications in combined-cycle power plants, petrochemical complexes, steel mills, refineries, and desalination units, while analyzing its key features, design parameters, performance factors, and economic considerations.
Horizontal HRSG
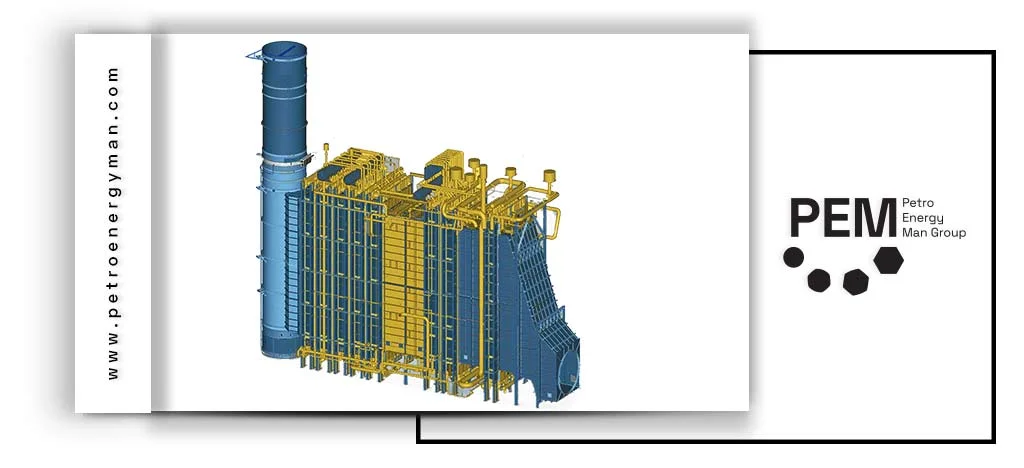
Horizontal Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG) systems guide exhaust gases horizontally across vertical tubes. In this configuration, hot gases leaving the gas turbine enter the HRSG chamber horizontally and pass sequentially through different sections such as the superheater, evaporator, and economizer. The arrangement of the tubes is critical: tubes containing water and steam are positioned vertically within the horizontal gas flow. This tube layout allows horizontal HRSGs to maximize the benefits of natural circulation, ensuring efficient heat transfer and optimal boiler performance.
Technical and Economic Advantages of Horizontal HRSG
The horizontal HRSG design offers numerous operational and engineering benefits, making it ideal for integration with advanced gas turbines and enhancing overall efficiency.
Cold-Casing Design
One of the key features of horizontal HRSGs is the cold-casing design. In this configuration, the outer shell is fully insulated, and internal plates are attached with stainless steel to provide enhanced protection and stability.
• Thermal Expansion Control: Internal plates allow differential movement between the hot internal sections and the cooler outer casing, reducing channel expansion.
• High-Temperature Resistance: Ensures safe operation of the HRSG at elevated temperatures.
• Rapid Start-Up: Better management of thermal stresses allows the turbine to start without causing structural damage.
As a result, this design not only guarantees the stable operation of the HRSG but also makes it fully compatible with advanced gas turbines operating at high temperatures and high efficiency.

Enhanced Efficiency and Operational Performance
Horizontal HRSG systems, in addition to high heat recovery efficiency, provide significant operational benefits. The design of single-pass (HOT) models ensures easy temperature control and maintains efficiency even under partial load or high ambient temperatures. In advanced horizontal designs, especially the Once-Through type, operation at higher pressures than standard vertical boilers is possible, improving overall system performance.
Moreover, the horizontal layout allows easier access to internal sections such as the furnace, flue path, and drum, simplifying inspection and maintenance while reducing operational costs. The combination of flexibility, high-pressure capability, and ease of maintenance makes horizontal HRSGs a reliable and efficient choice for advanced power plants.
Construction and Installation
Horizontal HRSG systems are often designed in a modular format, which offers several operational advantages, especially for horizontal models. With modular design, boiler components are assembled in the factory before being transported to the installation site, reducing fabrication time and simplifying the production process.
On-site installation is also faster, easier, and safer using this approach. Additionally, the combination of horizontal gas flow, finned tubes, and compact design significantly reduces the installation footprint, operational costs, and overall project duration.
Industrial Applications of Horizontal HRSG
Horizontal HRSG systems are widely used as effective heat recovery and steam generation units due to their high reliability and customizable steam parameters across various industries.

Combined Cycle and Cogeneration Power Plants
Horizontal HRSG units are primarily employed in combined cycle power plants. In these systems, the waste heat from the gas turbine exhaust is converted into steam at the required pressure and temperature. This steam is then used to drive a separate steam turbine, significantly improving the overall thermal efficiency of the power plant.
In addition to electricity generation, horizontal HRSGs are extensively applied in combined heat and power (CHP / cogeneration) systems. Here, the generated steam not only powers the steam turbine but also serves industrial process needs, district heating networks, and heating requirements for production lines.
The horizontal design ensures that hot gases flow efficiently through all modules, finned tubes increase the heat transfer surface, and steam pressure is precisely controlled. These features optimize the performance of the unit in large power plants and complex industrial projects.
Specialized Industrial Applications
Horizontal HRSG units are used to recover waste heat in the oil, gas, and petrochemical industries. These systems can capture residual heat from very high-temperature sources, such as diesel engines or ash-laden furnaces, and convert it into steam with controlled pressure and temperature.
In heavy industries like refineries, petrochemical plants, steel, and cement factories, the generated steam is directly used for industrial processes, supporting stable operation of production lines.
Horizontal HRSGs also supply the necessary steam for water treatment and desalination plants, particularly in regions such as the Persian Gulf, where centralized energy resources are available.
From an operational capacity perspective, these HRSGs can operate in multi-pressure systems, supporting high-pressure steam production rates up to 480 tons per hour and operating pressures up to 15.4 MPa. These specifications demonstrate their ability to integrate with large gas turbines and reliably meet extensive industrial steam demands.

Key Features of Horizontal HRSG
Horizontal HRSGs possess several distinct features that make them suitable for specialized industrial applications:
Horizontal Gas Flow: Exhaust gases from the turbine pass horizontally through the tube assembly, which is why this type of HRSG is referred to as “horizontal.”
Vertical Heat-Exchange Tubes: Tubes carrying water and steam are arranged vertically to optimize flow and heat transfer.
Top Supported Design: Many horizontal tube designs are supported from the top, allowing thermal expansion to move freely downward and reducing thermal stresses.
Cold Casing Design: The HRSG outer casing remains cool thanks to internal insulation. This design helps control thermal expansion and minimizes internal stresses.
Material Variations: The use of high-strength steels such as T22 in the superheater and reheater sections reduces tube thickness and improves resistance to fatigue caused by thermal cycles.
Modular Design: Horizontal HRSG units are often designed modularly, enabling faster installation and up to 20% reduction in start-up time.
Factors Affecting Horizontal HRSG Design
In the design of a horizontally configured HRSG, a set of key factors must be thoroughly evaluated and considered.
Operational and Environmental Parameters
Several operational and environmental factors play a critical role in the design of HRSG systems.
Gas Turbine and HRSG Load: Design must be coordinated with the output of the gas turbine and the requirements of the steam turbine to ensure optimal performance.
Exhaust Gas Characteristics: Temperature, pressure, and flow rate of the exhaust gas influence the size and configuration of the HRSG.
Cyclic Operation: Horizontal HRSG units must withstand frequent start-ups, shutdowns, and load changes without compromising performance or reliability.
Water and Steam Conditions: The flow rate, pressure, and temperature of water and steam are crucial for stable operation and safe start-up.
Standards and Regulations: Compliance with steam velocity, pressure limits, and pressure vessel codes is essential for drum design and overall system safety.

Geometric and Mechanical Specifications
Finned Tube Arrangement and Dimensions: The layout and dimensions of finned tubes—including diameter, height, thickness, and tube configuration—directly determine heat-transfer efficiency and pressure drop.
Horizontal HRSG Overall Dimensions and Drum Size: Horizontal HRSG design depends heavily on the overall length, width, and height of the unit, as well as drum dimensions, to ensure stable and efficient performance.
Modular Design: A modular configuration enables faster installation and provides flexibility for both power generation and combined heat and power (CHP) applications.
Wall Thickness of Pressure-Retaining Components: The wall thickness of pressure-bearing parts affects thermal stress control and impacts overall start-up time and operational durability.
Performance and Efficiency Factors
Thermal Efficiency: Optimizing thermal efficiency is essential for improving overall productivity and minimizing energy losses across the system.
Horizontal HRSG Gas-Side Pressure Drop & Heat-Transfer Rate: Horizontal HRSG performance depends on reducing flue-gas pressure drop and maximizing heat-transfer rate, achieved through advanced finned-tube configurations and enhanced gas-flow management.
Tube Temperature and Steam Outlet Control: Precise control of tube temperatures and outlet steam conditions prevents material fatigue and ensures reliable, safe operation.
Desuperheater Steam Injection System: The steam injection system in the desuperheater regulates both pressure and temperature of the outlet steam for stable and efficient performance.
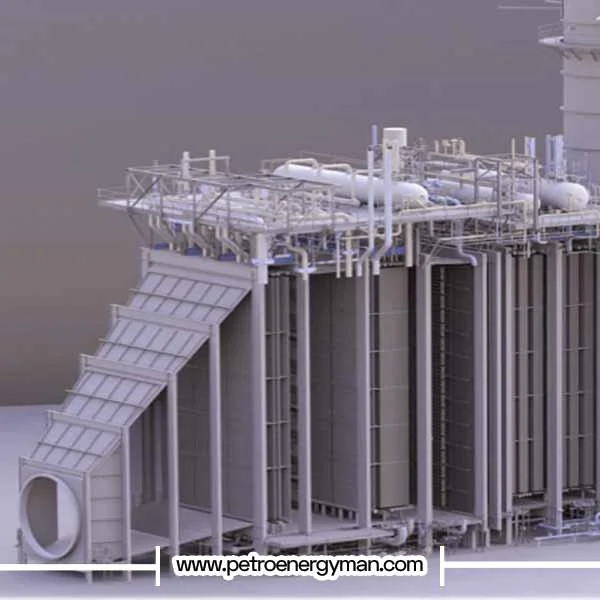
Economic and Reliability Factors
Initial Cost and Lifecycle Management: Optimizing the initial design and material selection plays a key role in reducing capital expenditure and minimizing long-term maintenance requirements.
Horizontal HRSG Reliability Performance: The reliability of a Horizontal HRSG directly impacts overall plant stability and operational efficiency, ensuring consistent performance under varying load conditions.
Overall System Optimization: Comprehensive integration of the HRSG design with the entire power plant supports seamless operation and enhances total system efficiency.
Conclusion
Horizontal HRSG serves as a strategic component within large-scale industrial facilities, and this article examined its critical aspects, including horizontal gas flow behavior, cold-casing structure, modular design advantages, major industrial applications, engineering characteristics, design considerations, and performance parameters. These capabilities enable the system to efficiently recover waste heat from gas turbines, generate stable steam across various pressure levels, and maintain reliable performance under demanding operating conditions. Ultimately, its ability to enhance energy efficiency, stabilize production processes, and reduce operational costs makes it an essential solution for modern power generation and high-demand industrial environments.



No comment