The price of a heat exchanger is influenced by a broad range of technical, economic, and market factors. A deep understanding of these parameters is essential for engineers, procurement managers, and investors to make optimal and cost-effective decisions. This article provides a detailed analysis of the most significant variables shaping the cost of these units. We will examine how exchanger type and design, construction materials, operating conditions, manufacturer reputation, and economic considerations together determine overall pricing structures. Ultimately, the purpose is to provide an analytical framework that facilitates informed decision-making in purchase and investment processes
Factors Influencing the Price of Heat Exchangers
The price of a heat exchanger is determined by a wide range of factors and parameters. These factors stem from the advanced engineering nature of these devices, their countless applications, and the direct impact of a combination of technical, economic, and market elements. This discussion focuses on the nature and mechanisms by which each factor exerts its influence. Instead of providing an exact price, it offers an analytical framework for understanding cost structures and making informed decisions in purchasing and investment processes.
The Impact of Technical and Design Factors on
Heat Exchanger Costs
The cost of heat exchangers is primarily affected by their technical features and design-related parameters. These include the type of exchanger, its capacity and physical dimensions, the material of construction, operating conditions, and the complexity of the internal design.
The choice of exchanger type is one of the key factors in cost determination. Differences in design complexity, manufacturing technology, raw material quality, and expected service conditions directly affect the final price.
The choice of exchanger type is one of the key factors in cost determination. Differences in design complexity, manufacturing technology, raw material quality, and expected service conditions directly affect the final price. For more information, you can refer to the Heat Exchanger
Exchangers with simpler designs and fewer components usually have lower initial costs, whereas advanced models with higher efficiency require more precise manufacturing processes and specialized materials, which increase their price.
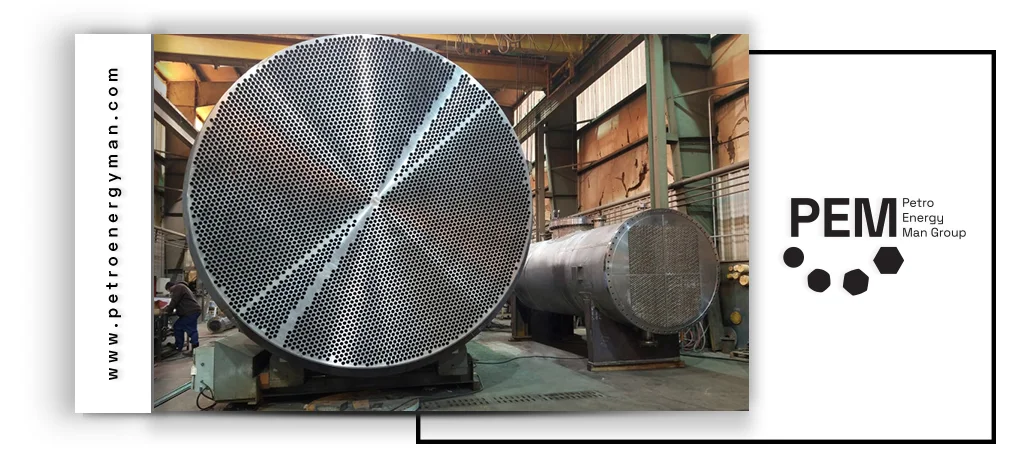
In addition to purchase price, operating and maintenance costs also represent an important part of the decision-making process. Some exchangers, despite having a higher initial cost, can reduce energy consumption and maintenance expenses over their service life due to better thermal efficiency, smaller footprint, and easier cleaning. Conversely, exchangers that require lower initial investment may generate higher long-term expenses because of lower efficiency or increased maintenance requirements.
Furthermore, any requirement for operation under special conditions—such as high pressure and temperature, viscous or corrosive fluids, or prevention of fouling—necessitates more complex designs and specialized materials, which increase costs. Life Cycle Cost (LCC) analysis is therefore the best method of comparison, as it does not focus solely on the purchase price but takes into account the total cost, including both capital and operational expenses, throughout the equipment’s lifetime.
Effect of material choice on cost
The selection of construction materials is one of the most critical factors influencing the final price of a heat exchanger. This choice is determined by the properties of the working fluids, operating temperature and pressure, and the required resistance to corrosion and fouling. Below is an overview of commonly used materials and special alloys:
- Stainless Steel (SS): Due to its high resistance to corrosion and heat, stainless steel is one of the most widely used materials. It is particularly suitable for fluids with corrosive properties. Various grades (SS304, SS316, SS321, SS347, SS410) are available, each offering distinct characteristics and cost levels. Plate heat exchangers and shell-and-tube exchangers are frequently manufactured from stainless steel.
- Copper: With its excellent thermal conductivity, copper is an efficient choice for rapid heat transfer. Copper heat exchangers are widely used in heating and cooling systems. Shell-and-tube copper exchangers are also popular in swimming pool applications, where their cost is largely determined by the quantity of copper tubing used.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and a good thermal conductor, aluminum is often applied in air-cooled heat exchangers and in certain automotive systems.
- Titanium: Known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, titanium is used in highly corrosive environments and at elevated temperatures. However, its high price significantly increases overall equipment costs.
- Special Alloys: These include Nickel (for caustic solutions), Incoloy (for hydrogen vapors with mercury and acids), Hastelloy (for sulfuric and nitric acids), and Titanium-Palladium alloys (for dilute sulfuric and nitric acid). Such materials are employed in highly aggressive applications and are generally associated with substantially higher costs.
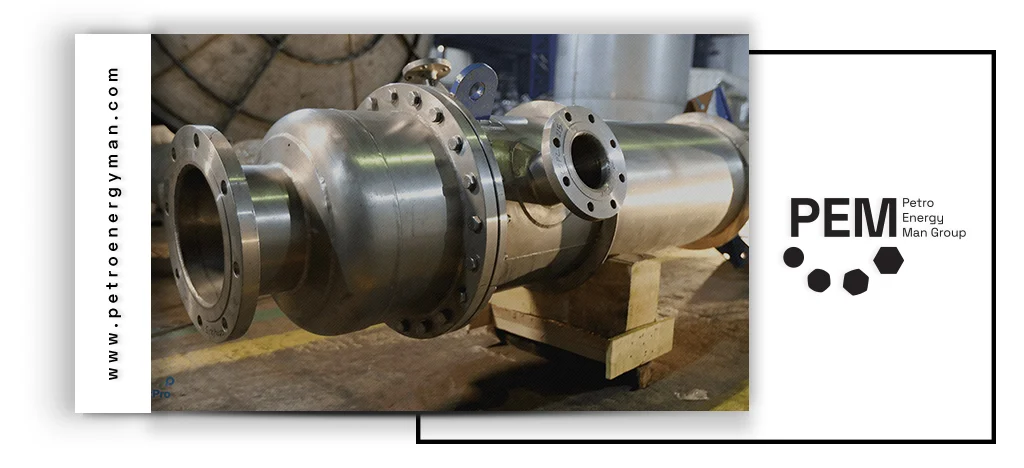
Impact of Operating Conditions and Fluid Properties on Cost
The price of a heat exchanger is directly influenced by operating conditions and the properties of the working fluid. High operating temperatures and pressures require the use of more durable materials and more complex designs, which increase manufacturing costs and the final price of the exchanger.
In particular, when dealing with corrosive fluids, high-viscosity media, or fluids containing suspended solids, the selection of expensive materials such as stainless steel, titanium, or nickel-based alloys, combined with specialized design considerations, significantly raises costs.
Additionally, to prevent fouling—which can reduce efficiency and increase maintenance expenses—advanced coating technologies and regular cleaning programs are required, adding further operational costs.
Therefore, the harsher the service conditions and the more aggressive the fluid properties, the greater the need for high-performance materials and complex designs, resulting in increased heat exchanger costs.
Design Complexity and Customization
In addition to the general type and material of construction, the cost of a heat exchanger is significantly influenced by internal design details and custom features. Factors such as the number of fluid passes increase thermal efficiency but also add complexity, thereby raising manufacturing costs.
The type of tube sheet, which secures the tubes, also impacts the exchanger price. For example, U-tube sheets generally have lower initial costs and are easier to maintain.
Furthermore, the design and quantity of baffles—which direct fluid flow and increase velocity—affect costs; the more complex and numerous the baffles, the higher the price. Additionally, tube arrangement and configuration, including the use of finned tubes to enhance heat transfer for fluids with low thermal conductivity, increase fabrication costs.
Therefore, detailed internal design features play a critical role in determining the final cost of a heat exchanger.

Impact of Manufacturer Brand and Reputation
The brand and reputation of a manufacturer are key factors in determining the price of heat exchangers. This factor affects not only the initial purchase price but also long-term value and operational costs. The influence of a reputable brand stems from its history, manufacturing technology, component quality, and after-sales support.
Well-established and recognized brands in the heat exchanger industry typically set higher prices for their products. This premium is not merely due to the brand name but reflects their substantial investment in research and development, the use of advanced manufacturing technologies, rigorous quality control at all production stages, and the application of high-grade raw materials. These factors result in products with higher performance, longer service life, and reduced maintenance requirements.
Moreover, reputable brands often provide strong after-sales support, reliable warranties, and assured availability of spare parts.In Iran, several companies are active in the design and manufacturing of heat exchangers, with some offering high-quality products at competitive prices and even exporting to neighboring countries.
The higher price of a reputable brand is therefore not simply for the name; it reflects their investment in R&D, strict quality control, superior raw materials, and dependable after-sales services. Such an investment ensures higher performance, extended lifespan, and lower maintenance needs. Purchasing from a reputable brand is thus a strategic decision that provides reliability and peace of mind, demonstrating its value over the long term by reducing hidden costs such as production downtime and unexpected repairs.
In addition to the technical and design factors discussed in detail, other variables—such as fluctuations in currency and raw material markets, skilled labor costs, industrial regulations and standards, and even transportation and installation conditions—also influence the final cost of heat exchangers.

Conclusion
The analysis of heat exchanger pricing indicates that the final cost depends on multiple interrelated variables, including design, exchanger type, heat transfer surface area, overall heat transfer coefficient, logarithmic temperature difference, construction material, operating conditions, and fluid properties, among others.
For professional consultation and to select the most suitable heat exchanger, contact PetroEnergyMan Holding at +98 21 57423000. Their team of experts will consider all technical and economic factors to recommend the optimal solution tailored to your needs.




No comment